Clubroot resistance canola cultivars development in Canada
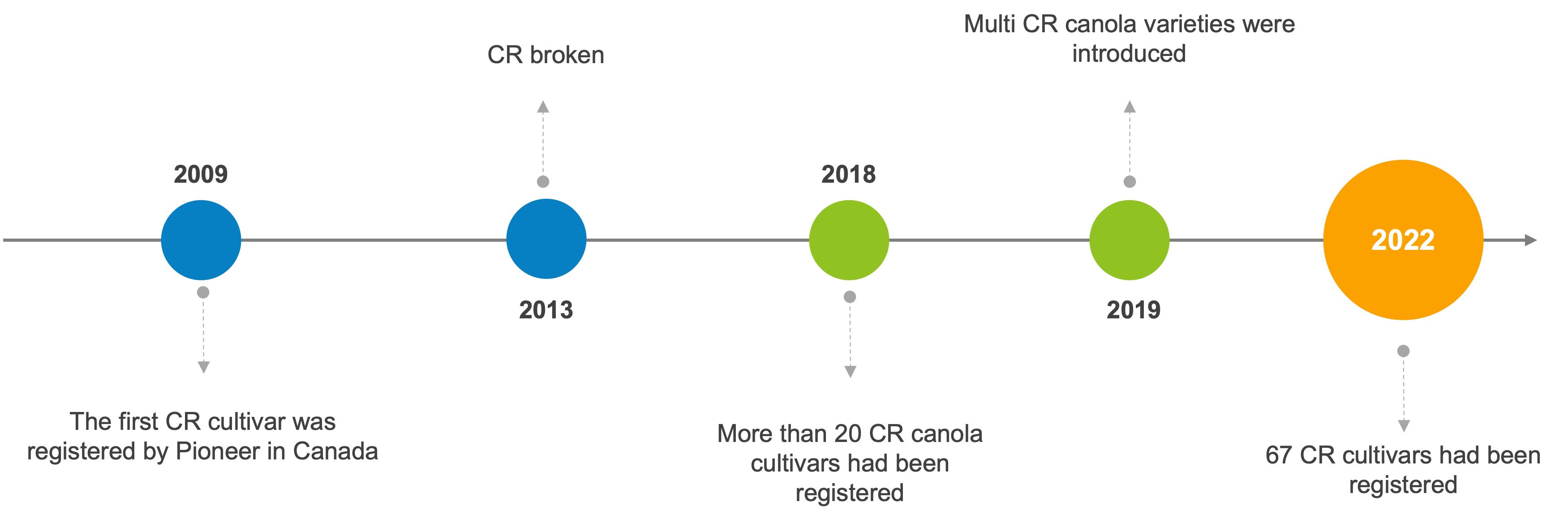
We have mentioned before that developing the clubroot resistance (CR) canola cultivar is one of the best management strategies. Canola growers in Canada rely on different genetic resistance resources to ensure the yield under pressure from emergence of novel pathotyoes of clubroot pathogen. Since the first CR canola cultivar has been introduced in Canada, there are more than 60 cultivars by different seed companies as of 2023. In this post, we are going to explore the history of different generations CR cultivars.
First-generation clubroot resistance
The first-generation of CR canola cultivars carry one single CR gene. The first CR cultivar named “45H29” and was developed by Pioneer in 2009, which carries one of the CR genes from the European resistance resource cv. Mendel (on chromosome A03). Subsequently, more resistant cultivars has been registered in following years, which are considered “first-generation” CR canola cultivars. It is reported that the first-generation of the CR cultivars can resist five of Canadian P. brassicae pathotypes 2, 3, 5, 6 based on Williams’ system.
Second generation clubroot resistance
Unfortunately, the pathogen P. brassicae continues to evolve putting the resistance of even these cultivars at risk. In 2013, new pathotypes (5X) in Alberta have been able to overcome first-generation of CR commercial canola cultivars. Subsequently, CR genes on chromosome A08 were found resistant to some of the novel pathotypes, which have recently been pyramided with those on A03 in several Canadian canola hybrids (second-generation) for a broader range of efficacy.
Although researchers and breeders have characterized multiple sources of resistance, implementing a multi-pronged approach to clubroot management remains a priority for growers and the canola industry.
References
https://www.ualberta.ca/folio/2023/08/new-clubroot-strains-continue-to-emerge.html
https://www.topcropmanager.com/new-clubroot-pathotypes-and-second-generation-resistance/
https://www.mdpi.com/2223-7747/12/4/726